A Brief American History Timeline
| 1600’s | 1920-1929 |
| 1700’s | 1930-1939 |
| 1800-1829 | 1940-1949 |
| 1830-1849 | 1950-1959 |
| 1850-1869 | 1960-1969 |
| 1870-1879 | 1970-1979 |
| 1880-1889 | 1980-1989 |
| 1890-1899 | 1990-1999 |
| 1900-1909 | 2000-2009 |
| 1910-1919 | 2010-Present |
1600’s
1607
English planters found Jamestown colony and complain about lack of laborers
 |
| Slave Trade Begins |
1619
Slave Trade Begins Slaves from Africa first imported to colonies
1620
Mayflower Compact signed creating “just and equal laws.”
1636
Maine Indentured Servants’ and Fishermen’s Mutiny
1648
Shoemakers and coopers (barrel-makers) guilds organize in Boston
1664
First slavery codes begin trend of making African servants slaves for life
1676
Bacon’s Rebellion of servants and slaves in Virginia
1677
First recorded prosecution against strikers in New York City
Top
1724
Carpenter’s Company of Philadelphia chartered to assist carpenter’s instruction and well-being.
1739
Stono Rebellion of slaves in South Carolina.
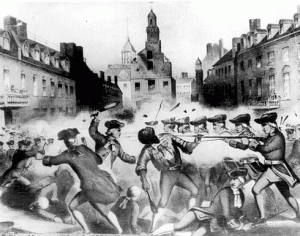 |
| The Boston Massacre |
1741
New York bakers quit work to protest local government setting the price of bread-possibly the first work stoppage in America
1765
The first society of working women, the Daughters of Liberty, is organized as an auxiliary of the Sons of Liberty, a workingman’s association
1768
New York tailors strike to protest a wage cut
1770
Boston Massacre set off by a conflict between rope workers and British soldiers
1775
A strike in Boston harbor, more commonly known as the “Boston Tea Party.” Local citizens dressed as Indians throw British tea overboard
1776
Declaration of Independence signed in Carpenter’s Hall
1778
New York printers combine temporarily to ask for a wage increase, disband after winning it
1786
Philadelphia printers strike
1790
First textile mill, built in Pawtucket, RI, is staffed entirely by children under the age of 12
1791
First Building Trades Strike: Philadelphia carpenters strike for a 10-hour day and overtime pay
1792
The first local craft union formed for collective bargaining was organized by shoemakers in Philadelphia
1794
The Philadelphia shoemakers reorganized as the Federal Society of Journeymen Cord Wainers.
The Typographical Society was formed by printers in New York City
1799
The Philadelphia shoemakers in a “sympathy strike” to support a local toolmakers’ strike
1800
Gabriel Prosser leads a slave revolt in Virginia
1805
A journeymen Cord Wainers’ union in New York City includes a closed-shop clause in its constitution
1806
Employers start taking labor groups to court for “criminal conspiracies in constraint of trade”. The shoemakers, found guilty and fined, went bankrupt and disbanded.
Members of the Philadelphia Journeyman Cord Wainers were tried for criminal conspiracy after a strike for higher wages
1814
The invention of the power loom makes weaving a factory occupation
 |
| Spinning mule |
1819
Depression begins
1822
Denmark Vesey leads a slave rebellion in South Carolina
1824
Women workers strike for the first time, in Pawtucket, Rhode Island. 102 women workers strike in support of brother weavers protesting the simultaneous reduction in wages and extension of the workday
1825
The United Tailoresses of New York, a trade union organization for women, organized in New York City.
1827
The Mechanics Union of Trade Associations, made up of skilled craftsmen in different trades, formed in Philadelphia – first city central federation.
Philadelphia Carpenters’ Strike
1828
Depression begins
First workingmen’s parties formed to try to elect candidates favoring the 10-hour day, free public education, and ending the practice of imprisoning people in debt
Paterson New Jersey, Textile Strike
1829
The Workingmen’s Party of New York formed
Carpenter Ebenezer Ford becomes the first trade unionist elected to public office in New York
Top
1831
New England Association of Farmers, Mechanics and other Workingmen formed.
February, 1600 women members of the United Tailoresses of New York, strike for “a just price for our labor.”
Nat Turner leads a slave rebellion in Virginia
 |
| Nat Turner |
Lynn, Massachusetts, Shoe Binders’ Protest
1832
Boston Ship Carpenters’ Ten Hour Strike
1833
Lynn, Massachusetts, Shoe Binders’ Protest begins
Manayunk, Pennsylvania, Textile Strike
New York City Carpenters’ Strike
1834
National Trades Union, first attempt at a national labor federation, formed in New York
Lowell, Massachusetts, Mill Women’s Strike
Manayunk, Pennsylvania, Textile Strike
1835
Ten-Hour Movement among skilled workers
Children employed in the silk mills in Paterson, New Jersey go on strike for the 11 hour day, 6 days a week.
1836
National Cooperative Association of Cord Wainers, the first national union of a specific craft, formed in New York City
Mill workers Lowell, Massachusetts,
 |
| Mill workers |
Mill Women’s Strike
New York City Tailors’ Strike
Philadelphia Bookbinders’ Strike
1837
Depression begins
Andrew Jackson declares a 10-hour workday in Philadelphia Navy Yard
1840
President Martin Van Buren establishes the ten-hour day for employees on federal public works projects.
1842
Massachusetts Supreme Court, in Commonwealth v. Hunt, rules that labor unions, as such, are not illegal conspiracies.
Anthracite Coal Strike
1845
The Female Labor Reform Association is formed in Lowell, Massachusetts by Sarah Bagley and other women cotton mill workers to reduce the work day from 12 or 13 hours a day to 10, and to improve sanitation and safety in the mills where they worked.
1847
New Hampshire passes first state law fixing ten hours as the legal workday.
1848
Pennsylvania’s child labor law makes twelve the minimum age for workers in commercial occupations.
1850-1869
1850
New York City Tailors’ Strike.
1852
Typographical Union founded – first national union of workers to endure to present day
 |
| Eugene V. Debs |
1855
Eugene V. Debs , US labor leader, is born
1859
Iron Molders’ International Union founded
1860
New England Shoemakers’ Strike
1861
Civil War Begins
American Miners’ Association , the first national coal miners’ union, is formed in St. Louis, Mo.
1862
Congress Passes the Homestead Act
1863
Emancipation Proclamation frees the slaves
Brotherhood of Locomotive Engineers founded
1864
Cigar Makers’ Union founded
1865
Thirteenth Amendment ratified, abolishing slavery in the United States
1866
National Labor Union founded – an attempt at creating a national federation of unions
Molders’ Lockout
1867
Knights of St. Crispin founded – a union of factory workers in the shoe industry
1868
First federal eight-hour law passed – applied only to laborers, workmen, and mechanics employed by the government
Anthracite Coal Strike
1869
Colored National Labor Union founded
Knights of Labor organized in Philadelphia
Troy, New York, Collar Laundresses’ Strike
Women shoemakers form the Daughters of St. Crispin, the first national union of women workers, at Lynn, Massachusetts.
1870-1879
1870
First written contract between coal operators and coal miners signed
1872
National Labor Reform Party formed
 |
| The Great Railroad Strike of 1877 |
1873
Depression begins
Miners’ National Association formed
1874
The union label is used for the first time by the Cigar Makers International Union
1875
A five-month long labor war in Pennsylvania between mostly Irish Coal Miners and the Reading Coal and Iron Company
1876
Trials of the “Molly Maguires”, a secret society of Irish coal miners in Pennsylvania that had been infiltrated by a Pinkerton detective, surrendered state sovereignty. A private corporation initiated the investigation through a private detective agency. A private police force arrested the alleged defenders, and private attorneys for the coal companies prosecuted them. The state provided only the courtroom and the gallows
1877
National Uprising of Railroad Workers cripples the nation in response to the cutting of wages for the second time in a year by the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad. The governor of West Virginia sends in state militia, but they refused to use force against the strikers and the governor called for federal troops. President Hayes sent federal troops from city to city. These troops suppressed strike after strike, until at last, approximately 45 days after it had started, the strike was over.
“Rope Day” ten leaders of the Molly Maguires were hanged
1880-1889
1881
Atlanta, Georgia: 3,000 Black women laundry workers stage one of the largest and most effective strikes in the history of the south
1882
September, First Labor Day Celebration takes place in New York City
 |
| Haymarket Riot |
1883
Pendleton Act established the United States Civil Service Commission, which placed most federal employees on the merit system and marked the end of the spoils or patronage system
1885
Knights of Labor Strike of South West System (J. Gould): The Missouri Pacific, the Missouri, Kansas and Texas; and the Wabash.
The Foran Act bans immigration of laborers brought in under contract to break strikes
1886
March, Great Southwest Railroad Strike of 200,000 workers against the Union Pacific and Missouri Pacific railroads owned by Jay Gould, one of the more flamboyant of the ‘robber baron’ industrialists of the day. The failure of the strike led directly to the collapse of the Knights of Labor and the formation of the American Federation of Labor.
Haymarket Tragedy: May 1, in Chicago’s Haymarket Square a bomb went off in the middle of a protest rally against the killing of 4 strikers who had been on strike for the 8-hour day.
The American Federation of Labor is formed at a convention in Columbus, Ohio, representing 140,000 workers grouped in 25 national unions. Sam Gompers is elected President
1888
Thomas W. Talbot and 18 other machinists met in a railroad engine pit in Atlanta, Ga. They formed the Order of United Machinists and Mechanical Engineers of America, now the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers.
The first federal labor relations law was enacted, applying to Railroad workers. It provided arbitration and Presidential boards of investigation
1890-1899
1892
The Great Homestead Lockout at the Carnegie Steel Works outside Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania against the Amalgamated Association of Iron, Steel & Tin Workers. Carnegie directs his manager, Frick, not to renew the union contract. Frick turns mills into “Fort Frick,” hires Pinkertons to protect scabs and locks out union laborers. Strikers battle arriving Pinkertons (9 strikers and 7 Pinkertons killed).
 |
| Cripple Creek Miners prisoners of the military |
Integrated general strike of 42 unions in New Orleans, broken when Governor Foster sends in the State Militia to use military force against the strikers.
Mary Kenney O’Sullivan of the Bindery Workers is appointed the AFL’s first female national organizer
1893
In the Cripple Creek Strike, Colorado gold miners, represented by the Western Federation of Miners are able to negotiate a peaceful end to a pitched battle between unionists and the state militia
1894
Eugene V. Debs leads the newly formed American Railway Union in a national strike against the Pullman Company. The strike and the union were finally broken by a court injunction and the intervention of federal troops
1898
Spanish-American War begins
Congress passes the Erdman Act, a more detailed version of the 1888 Railroad workers legislation, adding sections to make it illegal to fire workers for their union membership
American Labor Union founded
Marlboro, Massachusetts, Shoe Workers’ Strike begins
1899
Brotherhood of Teamsters founded
Buffalo, New York, Grain Shovelers’ Strike
Cleveland, Ohio, Street Railway Workers’ Strike
Coeur d’Alene, Idaho, Miners’ Strike
Top
1900-1909
1900
International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union founded
Anthracite Coal Strike
 |
| Mother Jones the Miners Angel |
Machinists’ Strike
1901
Socialist Party of America founded
United Textile Workers founded
Machinists’ Strike
National Cash Register Strike
San Francisco Restaurant Workers’ Strike
Steel Strike
1902
Great Anthracite Coal Strike , 147,000 miners strike over union recognition. Pres. Roosevelt mediated miners walk off the job for 164 days
Chicago Teamsters’ Strike
Big Bill Haywood leads the Western Federation of Miners (WMF) through a terrible and bloody series of conflicts spanning two years in what became known as the Colorado Labor Wars
1903
Mary Harris “Mother” Jones leads a protest march of mill children, many of whom were victims of industrial accidents, from Philadelphia to New York
Department of Commerce and Labor created by Congress
 |
| Miners |
Women’s Trade Union League founded
Cripple Creek, Colorado, Miners’ Strike begins
Oxnard, California, Sugar Beet Strike
Telluride, Colorado, Miners’ Strike begins
Utah Coal Strike begins
1904
New York City Interborough Rapid Transit Strike
Packinghouse Workers’ Strike
Santa Fe Railroad Shopmen’s Strike begins
1905
In Chicago, Eugene Debs and Big Bill Haywood combine efforts to found the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW or Wobblies as they were called) to bring all American workers into “One Big Union
New York Supreme Court, in Lochner v. New York, declares maximum hours law for bakers unconstitutional 1906
Eight-hour day widely installed in the printing trades
1906
The International Typographical Union successfully strikes for an 8-hour day
1907
Goldfield, Nevada, Miners’ Strike begins
An explosion kills 361 miners in Monongah, West Virginia in the nation’s worst mining disaster
1908
President William Howard Taft elected
Federal court, in US v. Adair, finds section of the Erdman Act banning yellow-dog contracts unconstitutional
US Supreme Court, in Danbury Hatters Case, holds a boycott by the United Hatters Union against a manufacturer to be a conspiracy in restraint of trade under the Sherman Antitrust Act
US Supreme Court, in Muller v. Oregon, declares an Oregon law limiting working hours for women unconstitutional
IWW Free-Speech Fight in Missoula, Montana
1909
National Association for the Advancement of Colored People founded
Georgia Railroad Strike
IWW Free-Speech Fight in Spokane, Washington
McKees Rocks, Pennsylvania, Steel Strike
“Uprising of the 20,000” Garment Strike in New York
Watertown, Connecticut, Arsenal Strike
Canada establishes Department of Labour due to union pressure
1910-1919
1910
Bethlehem Steel Strike
 |
| Fire Engine Races to the Triangle Shirtwaist fire. 146 women die. |
Cloak makers’ Strike
Chicago Clothing Workers’ Strike, led by fifteen year old Bessie Noramowitz
Los Angeles strike wave
Philadelphia General Strike
The wives of striking miners arrested in Greensburg, Pennsylvania sing their way out of jail under the leadership of Mother Jones
1911
US Supreme Court, in Gompers v. Bucks Stove and Range Company, upholds an injunction ordering the AFL to remove the company from its unfair list and cease a boycott.
Fire kills 146 workers at the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory in New York City.
Illinois Central and Harriman Lines Rail Strike begins
Southern Lumber Operators’ Lockout begins
1912
President Woodrow Wilson elected
Massachusetts adopt the first minimum wage act for women and minors.
Chicago Newspaper Strike
Fur Workers’ Strike
IWW Free-Speech Fight in San Diego, California
Lawrence, Massachusetts, Textile Strike, twenty thousand textile workers representing 26 different nationalities win the 60 day “Bread and Roses” strike
Louisiana Timber Workers’ Strike begins
New York City Hotel Strike
Pain Creek and Cabin Creek, West Virginia, Mine Strikes
 |
| 20,000 Strikers in 1912 Bread and Roses Strike |
1913
US Department of Labor established
Ludlow, Colorado, Massacre
Machinists Strike and Boycott
Michigan Copper Strike
Paterson, New Jersey, Textile Strike
Rubber Workers’ Strike
Studebaker Motors Auto Workers’ Strike
Wheatland, California, Hop Riot
1914
Congress passes the Clayton Antitrust Act. Ostensibly limits the use of injunctions in labor disputes
Amalgamated Clothing Workers founded
 |
| Monument to Murdered Strikers and Family Members in Ludlow, Co |
Fulton Bag and Cotton Mill Strike begins
Company gunmen attack a tent colony of striking UMWA families in Colorado and kill 19 men, women, and children in the Ludlow Massacre
1915
Congress passes the LaFollette Seamen’s Act – regulates working conditions for seamen
Standard Oil Strike
Youngstown, Ohio, Steel Strike begins
Joe Hill , IWW union organizer, executed in Salt Lake City on trumped up murder charge
1916
Congress passes Federal Child Labor Law – later declared unconstitutional
Congress passes the Adamson Act establishing the eight-hour day for railroad workers
Six killed and forty wounded in bombing of San Francisco preparedness parade – labor leaders arrested
American Federation of Teachers founded
Arizona Copper Strike
Everett, Washington, Massacre
Minnesota Iron Range Strike
New York City Transit Strike
New York Cloak makers’ Strike
San Francisco Open Shop Campaign
Standard Oil Strike
1917
United States enters World War I
Supreme Court, in Hitchman Coal and Coke v. Mitchell, upholds the legality of yellow-dog contracts
Green Corn Rebellion in Oklahoma
Tom Mooney sentenced to death for role in San Francisco preparedness parade bombing.
Bisbee, Arizona, Miners’ Strike
 |
| Many Young Children were Killed or Crippled before Child Labor became illegal in the US. |
Butte, Montana, Miners’ Strike
East St. Louis Race Riot
Pacific Northwest Lumber Strike
1918
War Labor Board is created
Keating-Owen Act bans child labor; annulled by Supreme Court Many Young Children were Killed or Crippled before Child Labor became illegal in the US.
World War I ends
Leadership of the Industrial Workers of the World sentenced to federal prison on charges of disloyalty to the United States
First national conference of women trade unionists
1919
Huge postwar strike wave sweeps across the nation
Communist Party of America founded
Red Scare begins
Actors’ Strike
Boston Police Strike
Centralia, Washington, Massacre
Chicago Race Riot
New England Telephone Strike
Seattle General Strike
16,000 Silk Workers in Paterson, NJ strike for a shorter workweek
Steel Strike
Winnipeg General Strike in Canada
1920-1929
1920
President Warren Harding elected
More than four thousand alleged Communists arrested for deportation under “Anarchist Exclusion” Act of 1918; DOL refuses to deport the bulk of those arrested; Secretary Wilson threatened with impeachment.
Trade Union Educational League founded
 |
| Coal Miners Turn In Guns in Matewan County |
Alabama Miners’ Strike
Clothing Workers’ Lockout
West Virginia Coal Wars begin, ten people killed in the Matewan Massacre in a battle over the right to organize the southern West Virginia coalfields
1921
Supreme Court, in Duplex Printing Press v. Deering, rules that the Clayton Act notwithstanding, federal courts could enjoin unions for actions in restraint of trade
Congress restricts immigration to the United States and establishes the national origin quota system
Seamen’s Strike
West Virginia Coal Wars and Baldwin-Felts agents kill West Virginia unionists Sid Hatfield an Ed Chambers on the steps of the McDowell County Courthouse
Battle of Blair Mountain, 2000 US troops block miners’ attempt to organize in southern West Virginia
1922
Conference for Progressive Political Action founded
Anthracite Coal Strike
Bituminous Coal Strike
Herrin, Illinois, Massacre
Nationwide railroad strike of 400,000 shop workers caused by the Railroad Labor Board’s wage cut. The railroads hired strikebreakers, increasing hostilities between the railroads and striking workers. On September 1 federal judge James H. Wilkerson issued a sweeping injunction against striking, assembling, picketing, and a variety of other union activities, colloquially known as the “Daugherty Injunction
1924
President Calvin Coolidge elected
Samuel Gompers dies. William Green becomes president of the American Federation of Labor
1925
Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters founded
Anthracite Coal Strike
1926
Congress passes the Railway Labor Act, which requires that employers bargain with unions and forbids discrimination against union members
Passaic, New Jersey, Textile Strike
 |
| Outside the NY Stock Exchange |
1927
Nicolo Sacco and Bartolomeo Vanzetti, Massachusetts labor activists are executed
Bituminous Coal Strike
Columbine Mine Massacre of striking coal miners in Colorado who were attacked with machine guns
1928
President Herbert Hoover elected
New Bedford, Massachusetts, Textile Strike
Convict-labor system for coal mining is outlawed in Alabama
1929
Stock market crash and the beginning of the Great Depression
Trade Union Unity League founded
Conference for Progressive Labor Action founded
Gastonia, North Carolina, Textile Strike
Top
1930-1939
1930
Mother Jones , UMWA organizer, dies at age 100
National Unemployed Council formed
Imperial Valley, California, Farm workers’ Strike
1931
Congress passes Davis-Bacon Act providing for payment of prevailing wages to workers employed on public works projects
“Scottsboro Boys” arrested in Alabama
 |
| Teamsters Battle Police in Minneapolis, MN. |
Harlan County, Kentucky, Miners’ Strike
Tampa, Florida, Cigar Workers’ Strike
1932
President Franklin Delano Roosevelt elected
Emergency Relief and Construction Act; created employment through a public works program.
Congress passes the Norris-LaGuardia Act, which prohibits federal injunctions in labor disputes and outlaws yellow-dog contracts
Bonus March of World War I veterans on Washington, DC
American Federation of Government Employees founded
California Pea Pickers’ Strike
Century Airlines Pilots’ Strike
Davidson-Wilder, Tennessee, Coal Strike begins
Ford Hunger March in Detroit, Michigan
Four workers killed as protesters march on Ford Rouge Plant near Detroit seeking jobs during the Great Depression
Vacaville, California Tree Pruners’ Strike
1933
Congress passes the National Industrial Recovery Act, Section 7(a) of which guarantees rights of employees to organize and bargain collectively
Civilian Conservation Corps established; DOL assists with administration.
Frances Perkins becomes secretary of labor and the first woman named to a presidential cabinet
Newspaper Guild founded
Briggs Manufacturing Strike
 |
| Colorado Miners Poster |
California Farm workers’ Strikes
Detroit, Michigan, Tool and Die Strike
Hormel, Iowa, Meat-Packing Strike
New Mexico Miners’ Strike
1934
Southern Tenant Farmers’ Union founded
Harlem, New York City, Jobs-for-Negroes Boycott
Imperial Valley, California, Farm workers’ Strike
Minneapolis Teamsters’ Strike
Newark Star-Ledger Newspaper Strike begins
Rubber Workers’ Strike
San Francisco Longshoremen & General Strike
Textile Workers’ Strike
Toledo, Ohio, Auto-Lite Strike
1935
US Supreme Court declares the National Industrial Recovery Act unconstitutional
Congress passes the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA), which protects the rights of workers to organize and bargain collectively.
FD Roosevelt signs the labor-backed Social Security Act into law
Committee for Industrial Organization (CIO) formed inside the American Federation of Labor
Negro Labor Committee founded
United Auto Workers founded
Oklahoma, Kansas and Missouri Metal Workers’ Strike
Pacific Northwest Lumber Strike
Southern Sharecroppers’ and Farm Laborers’ Strike
1936
President Franklin Roosevelt reelected
Steel Workers’ Organizing Committee formed
Atlanta, Georgia, Auto Workers’ Sit-Down Strike
Berkshire Knitting Mills Strike
First sit-down strike by auto workers starts at Bendix Products in South Bend, Indiana
General Motors Sit-Down Strike
RCA Strike
Rubber Workers’ begin the nation’s first major sit-down strike at the Firestone tire plant in Akron, Ohio
Seamen’s Strike
Seattle Post-Intelligencer Newspaper Strike
1937
US Supreme Court declares the NLRA constitutional
American Federation of Labor expels the CIO unions
American Federation of State, County and Municipal Employees union founded
General Motors Sit-Down Strikes in US and Canada – strikes end after workers win first UAW contract
Battle of the Overpass, Ford Motor Co. thugs beat Walter Reuther and other UAW organizers in Dearborn, Michigan
Hershey, Pennsylvania, Chocolate Workers’ Strike
 |
| Sit Down Strikers at Flint MI Ford Plant |
Little Steel Strike and Memorial Day Massacre, ten strikers shot at Republic Steel in Chicago
US Steel signs a first contract with the Steel Workers Organizing Committee
1938
Congress passes the Fair Labor Standards Act, which establishes the forty-hour work week, the minimum wage, and bans child labor in interstate commerce
Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO) is founded with John L. Lewis as president
John L. Lewis, seeking to organize steelworkers, secures a labor contract with the president of the world’s largest steel company, United States Steel, but the smaller companies that collectively were known as “Little Steel” brutally fought steelworkers. Scores of deaths and injuries occurred as the United Steelworkers of America struck at Little Steel plants across the industrial northeast
Chicago Newspaper Strike begins
Hilo, Hawaii, Massacre
Maytag Strike
US Supreme Court issues decision permitting employers to permanently replace strikers
1939
Chrysler Auto Strike
General Motors Tool and Die makers’ Strike
1940-1949
1940
President Franklin Roosevelt reelected
 |
| President Roosevelt |
Philip Murray replaces John L. Lewis as CIO president
Ford Motor Strike
1941
United States enters World War II
Walt Disney Animators strike
AFL and CIO give no-strike pledges for the duration of the war
Allis-Chalmers Strike
Captive Coal Mines Strike
Detroit, Michigan, Hate Strike against black workers
International Harvester Strike
New York City Bus Strike
North American Aviation Strike
1942
National War Labor Board is established – establishes the “Little Steel Formula” for wartime wage adjustments
United Steel Workers of America founded
1943
Fair Employment Practices Committee is established
Congress passes the Smith-Connally Act to restrict strikes and union political activity during the war
Bituminous Coal Strike, UMWA strike which triggered a US government takeover of the mines ends with a contract providing portal-to-portal pay and other benefits
Detroit, Michigan, Hate Strikes against black workers
 |
| Disney Animators on Strike |
Detroit, Michigan, Race Riot
1944
President Franklin Roosevelt reelected
Philadelphia Transit Strike
1945
President Franklin Roosevelt dies
Vice-President Harry S. Truman becomes President
World War II ends
1945
Kelsey-Hayes Strike
New York City Longshoremen’s Strike
Montgomery Ward Strike
Oil Workers’ Strike
1946
Huge postwar strike wave sweeps across the nation
United Mine Workers win a health and welfare fund in bargaining with the coal operators
Nationwide coal strike prompts US government to seize the mines to continue production
Electrical Manufacturing Strikes
General Motors Strike
 |
| Unions Promise Not to Strike to Support the War Effort. |
Pittsburgh Power Strike
Railroad Strike
Steelworkers launch 30 state strike against US Steel
1947
Congress passes the Taft-Hartley Act (Labor Management Relations Act) restricting union practices and permitting the states to ban union security agreements.
RJ Reynolds Tobacco Company Strike
Telephone Strike
1948
President Harry S. Truman is reelected
Progressive Party formed
1949
CIO expels two unions for alleged Communist domination
Hawaii Dock Strike
Top
1950-1959
1950
United States enters Korean War
CIO expels nine unions for alleged Communist domination
 |
| George Meany |
United Auto Workers and General Motors sign a contract that provides for pensions, automatic cost-of-living wage adjustments, and guaranteed increases over the life of the contract
“Salt of the Earth” Strike of New Mexico Miners begin
1951
UAW president Walter Reuther elected president of CIO
1952
President Truman seizes the steel industry when the steel companies reject the Wage Stabilization Board recommendations. Supreme Court rules the action unconstitutional
George Meany becomes president of the AFL
Walter Reuther becomes president of the CIO
President Dwight D. Eisenhower is elected
Steel Strike
1953
AFL and CIO agree to a “no raiding” pact. AFL expels the International Longshoremen’s Association for corruption
Louisiana Sugar Cane Workers’ Strike
 |
| Kohler Strikers |
1954
Kohler Strike begins
1955
United Auto Workers win supplementary unemployment benefits in bargaining with Ford
AFL and CIO merge with George Meany as first president, UMWA remains independent
Southern Telephone Strike
1956
President Dwight D. Eisenhower is reelected
East Coast Longshoremen’s Strike
Steel Strike
Canadian Labour Congress founded
1957
AFL-CIO expels Teamsters, Bakery Workers, and Laundry Workers for corruption
1959
Congress passes the Labor-Management Reporting and Disclosure Act (Landrum-Griffin), which regulates the internal affairs of unions
Longest steel strike in U.S. history, shut down 90% of US steel production for 116 days
1960-1969
1960
President John F. Kennedy is elected
Civil rights sit-in begins at Woolworth’s lunch counter in Greensboro, North Carolina
Negro American Labor Council founded
General Electric Strike
Seamen’s Strike
1962
Presidential executive order gives federal employee’s unions the right to bargain with government agencies
New York City Newspaper Strike begins
East Coast Longshoremen’s Strike
1963
President John F. Kennedy is assassinated
Vice-President Lyndon B. Johnson becomes President
Congress passes Equal Pay Act prohibiting wage differentials based on sex for workers covered by the Fair Labor Standards Act
1964
President Lyndon B. Johnson is reelected
 |
| Dr. Martin Luther King Murdered While Supporting Strikers |
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act bars discrimination in employment on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin
Teamsters President Jimmy Hoffa succeeds in bringing virtually all North American over-the-road truck drivers under a single national master freight agreement
1965
United Farm Workers Organizing Committee formed
California Grape Workers’ Strike
1966
New York City Transportation Strike
1967
Copper Strike begins
1968
President Richard M. Nixon is elected
Civil Rights leader Martin Luther King, Jr., is assassinated while supporting a strike by Memphis, Tennessee, sanitation workers.
New York City Teachers’ Strikes
November 20th, a gas explosion at Consolidated Coal Company’s No. 9 mine at Farmington, West Virginia trap 81 men, 78 of whom are killed in the mine.
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act makes it illegal to discriminate against people 40 to 65 years old
1969
Charleston, South Carolina, Hospital Workers’ Strike
Black Lung compensation bill passes in West Virginia after mass demonstrations by UMWA members
Top
1970-1979
1970
Postal strike is first nationwide strike of public employees
Hawaii becomes the first state to allow local and state government employees the right to strike
Congress passes the Occupational Safety and Health act
General Motors Strike
Postal Workers’ Strike , President Nixon declares a national emergency and orders 30,000 troops to New York City to break the first nationwide postal strike
Federal Coal Mine Health and Safety Act takes effect after passing Congress December 30, 1969
1971
New York City Police Strike
 |
| Cesar Chavez |
1972
President Richard M. Nixon is reelected
Farah Clothing Workers’ Strike and Boycott
Lordstown, Ohio, Auto Workers’ Strike
Philadelphia Teachers’ Strike begins
Quebec workers general strike
1973
United Farm Workers, led by Cesar Chavez and Dolores Huerta, is chartered by the AFL-CIO
1974
Coalition of Labor Union Women is founded (CLUW)
Congress passes the Employment Retirement Income Security Act regulating all private pension plans
Baltimore Police Strike
Oil, Chemical, and Atomic Workers union activist Karen Silkwood is killed during investigation of Kerr-McGee nuclear plant in Oklahoma
1975
First legal statewide public employees’ strike in nation’s history occurs in Pennsylvania
Congress defeats a union-sponsored attempt to reform the nation’s basic labor law
Washington Post Pressmen’s Strike begins
1976
President Jimmy Carter is elected
Congress defeats a union-sponsored attempt to have a law enacted that would improve the ability of construction unions to organize and carry out effective strikes
More than 1 million Canadian workers demonstrate against wage controls
1977
Bituminous Coal Strike begins
Coors Beer Strike and Boycott begins
J.P. Stevens Boycott begins
Willmar, Minnesota, Bank Workers’ Strike
1978
Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Newspaper Strike begins
1979
Lane Kirkland becomes president of the AFL-CIO
Independent Truckers’ Strike
Top
1980-1989
1980
President Ronald Reagan is elected President of the United States of America
Joyce Miller of the International Ladies’ Garment Workers’ Union becomes the first woman to sit on the AFL-CIO executive board
1981
President Ronald Reagan fires most of the nation’s air traffic controllers for striking illegally and orders their union, the Professional Air Traffic Controllers Association, decertified.
400,000 unionists, the largest labor rally in American history takes place in Washington in protest against the policies of the Reagan administration
 |
| Striking PATCO Workers |
Baseball Players’ Strike
1983
Phelps-Dodge Copper Strike begins
1984
President Ronald Reagan is reelected President of the United States of America
Yale University Clerical Workers’ Strike
1985
Hormel Meatpackers’ Strike begins
Los Angeles County Sanitation District Strike
Yale University Clerical Workers’ Strike
1986
Trans World Airlines Flight Attendants’ Strike
USX (United States Steel) Lockout begins
1987
Professional Football Players’ Strike
1988
60,000 Home Care Workers Strike in NY
President George Bush is elected President of the United States of America
1989
Eastern Airlines Workers’ Strike
Mine Workers’ Strike against Pittston Coal Company
1990-1999
1990
UMWA Pittston Strike ends, miners ratify a new contract
Delta Pride Catfish Workers Victory
1991
Three hundred thousand unionists march in Washington, DC to demand workplace fairness and health care reform
Twenty five workers die in a fire at the nonunion Imperial Food plant in Hamlet, North Carolina , which had never been inspected by federal or state agencies
 |
| Locked Fire Exit at Non-Union Plant. Twenty Five People Died in a Fire at the Imperial Food plant. |
Hotel Normandy Strike
1992
Bill Clinton is elected President of the United States of America
Caterpillar Strike
Justice for Janitors Century City Demonstration – police attack
1993
Staley Workers’ Lockout in Decatur
A five day strike of 21,000 American Airlines’ flight attendants, virtually shutting the airline down is ended when Pres. Clinton persuades the owners to arbitrate the dispute
The Family and Medical leave Act is passed
North American Free Trade Agreement Passes
April 23, 1993, Cesar E. Chavez dies at the age of 66
1994
The longest players’ strike in sports history (232 days) is conducted by the Major League Players Association against National and American League owners
1996
Bill Clinton is reelected President of the United States of America
1997
In a big win for their members and all of organized labor, the Teamsters reach a new five-year agreement with United Parcel Service (UPS) on Aug. 18, ending a two-week strike over abuse of part-time workers and health care for retirees
2000-2009
2001
The 500,000-member United Brotherhood of Carpenters and Joiners announced that it was disaffiliating with the national AFL-CIO because of differences in the direction of the labor movement.
 |
| 27,000 Boeing IAM members strike against a proposed two tier pay scheme. |
10,000 Public school teachers and 3000 state university faculty in Hawaii shut down all public education in the State in the nation’s first state-wide education strike
2004
70,000 Southern California grocery workers strike Safeway to protect their health benefits and s imposition of a vicious two-tier wage system
2005
Seven major national unions, representing six million workers, disaffiliate from the AFL-CIO and, in September, form a new coalition called “Change to Win”, devoted to organizing
2006: After years of one of the most anti-labor Congresses in decades, strong voter turnout by union members helps put a pro- labor majority in control of the U.S. House of Representatives and a razor-thin majority in the U.S. Senate.
2008
27,000 Machinists union members strike Boeing for 57 days. “The strike was triggered by a Boeing strategy to create a separate and lower class of employees in its manufacturing facilities; one with lower pay, fewer benefits and a cut-rate retirement plan,” said IAM President Tom Buffenbarger.
2008:
Barack Obama becomes the first African-American elected President of the United States. Labor voters again play a key role in national elections, increasing the pro-labor majorities in the House of Representatives and U.S. Senate and a pro-labor president. Pro-labor candidates win key governorships and
legislative races.
2010
In January 2010, a decision handed down by the ultra-conservative majority on the U.S. Supreme Court allows unlimited spending by corporations in U.S. elections, opening the floodgates for corporate cash in the November elections. Pro- business candidates sweep midterm elections and take control of the U.S. House of Representatives, gain control of many state governorships and secure anti-worker majorities in many state legislatures.
2011
Pro-business governors and state legislators elected in 2010 start nationwide assault on unions by attacking the right to collectively bargain, proposing right-to-work (for less) laws and other measures to weaken unions. Mass protests erupt in Wisconsin and spread nationwide.
